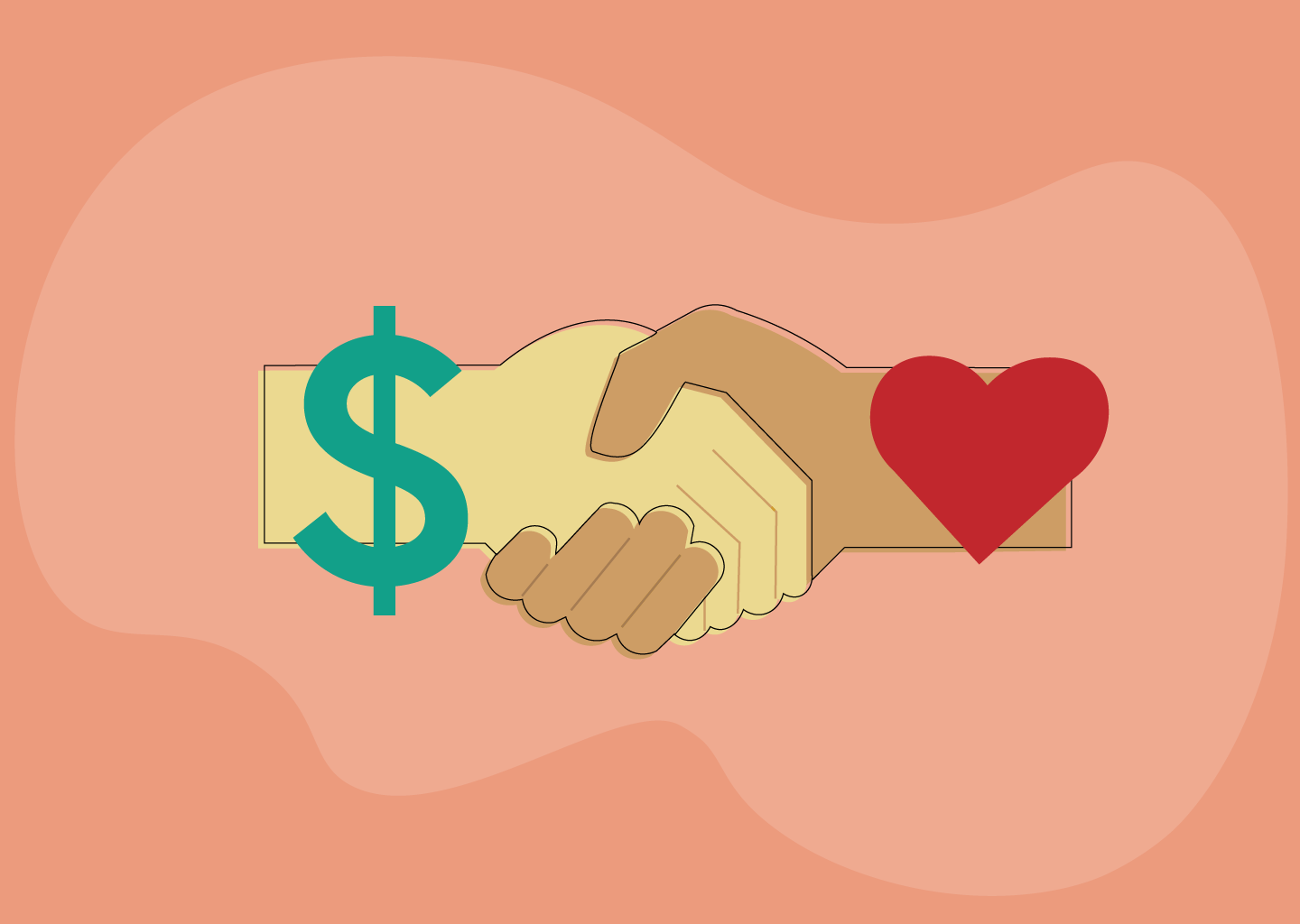

It is a marketing strategy that links a brand to a social or humanitarian cause with the aim of strengthening the relationship with customers by supporting a meaningful cause. This type of marketing seeks to achieve both commercial and social goals.
Characteristics:
1. Focus on values: Links the brand to a social cause or value, such as environmental protection, education, or human rights.
2. Partnership with non-profit organizations: Often requires cooperation between companies and non-profit organizations to achieve common goals.
3. Building trust: Aims to build trust and credibility with customers by demonstrating the company's commitment to social causes.
4. Engaging with the community: Encourages companies to actively participate in local communities.
Benefits:
1. Enhancing the company's public image: Supporting social causes is associated with improving the company's reputation and making it more attractive to customers.
2. Increased loyalty: Customers tend to be more loyal to brands that embrace causes they care about.
3. Attracting new customers: Cause marketing can attract customers who care about social causes and are looking for products that support these causes.
4. Differentiation from competitors: Allows companies to differentiate themselves from their competitors by associating the brand with a unique cause.
Pros:
1. Positive social impact: Allows companies to make a positive impact on society while generating profits.
2. Customer engagement: Increases customer engagement with the brand by making them part of meaningful initiatives.
3. Public relations: Can provide significant public relations opportunities thanks to media attention on social issues.
4. Value-added: Can provide added value to products and services by associating them with an important cause.
Cons:
1. Risk of inauthentic marketing: If a company does not demonstrate a genuine commitment to the cause, it can be seen as just a publicity stunt, which damages its credibility.
2. Cost: Partnerships with nonprofits and social initiatives can be expensive.
3. Difficulty in measurement: It can be difficult to accurately measure the return on investment in cause marketing campaigns.
4. Potential for negative backlash: If the cause the company supports is controversial, it may face negative reactions from some customers.
Examples of modern Arab companies that use cause marketing:
1. Zain: Zain supports many social initiatives such as education and supporting children in need.
2. PepsiCo Middle East: It has carried out campaigns to support clean water initiatives in remote areas in cooperation with non-governmental organizations.
3. Etisalat: It has supported campaigns to combat diseases such as breast cancer, and provided material and moral support to the relevant organizations.
Cause marketing is a strategy that combines commercial and social goals, where companies seek to support important causes while achieving commercial benefits. This type of marketing is a powerful way to enhance customer relationships and increase loyalty, but it requires a real commitment to the cause and the ability to deal with the challenges associated with it to ensure its success.

20/08/2024

14/08/2024

26/08/2024

01/09/2024

31/08/2024
18/08/2024

14/08/2024

18/08/2024

25/08/2024

15/08/2024
20/08/2024

26/08/2024

30/08/2024

30/08/2024

31/08/2024
18/08/2024

18/08/2024

18/08/2024

17/08/2024

30/08/2024